Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Yokoyama, Kenji; Hazama, Taira; Taninaka, Hiroshi; Oki, Shigeo
JAEA-Data/Code 2024-007, 41 Pages, 2024/10
The third version of the versatile reactor analysis code system, MARBLE3, has been developed. In the development of the former version of MARBLE, object-oriented scripting language Python (Python2) had been used and then the latest version of Python (Python3) was released. However, due to its backward incompatibility, MARBLE no longer worked with Python3. For this reason, MARBLE3 has been fully modified and maintained to work with Python3. In MARBLE3, newly developed analysis codes and newly proposed calculation methods were incorporated, and the user interface was extended and solvers were reimplemented for maintainability, extensibility, and flexibility. In MARBLE3, the three-dimensional hexagonal/triangular transport code MINISTRI Ver.7 (MINISTRI7) and the three-dimensional hexagonal/triangular diffusion code D-MINISTRI are available as the new analysis codes. These codes can be used in the neutronics analysis system SCHEME and the fast reactor burnup analysis system OPRHEUS, which are the subsystems of MARBLE. In addition, the user interface of CBG, a core analysis system embedded in MARBLE, was extended so that the diffusion and transport calculation solvers for the 2-dimensional RZ system of CBG can be used on SCHEME. On the other hand, MARBLE3 has extended the functionality of the burnup calculation solver so that it can use the numerical methods proposed in the papers on the improvement of the Chebyshev rational function approximation method and the minimax polynomial approximation method. From the viewpoint of maintainability, the point reactor kinetics solver POINTKINETICS, which was introduced in MARBLE2, has been newly reworked as the KINETICS solver in MARBLE3.
 Mg,
Mg,  Si,
Si,  Fe,
Fe,  Cu, and
Cu, and  Zn
ZnSugihara, Kenta*; Meigo, Shinichiro; Iwamoto, Hiroki; Maekawa, Fujio
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 549, p.165299_1 - 165299_12, 2024/04
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Instruments & Instrumentation)Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; National Institute for Materials Science*
JAEA-Review 2023-031, 101 Pages, 2024/01
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2022. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (1F), Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2020, this report summarizes the research results of the "Development of genetic and electrochemical diagnosis and inhibition technologies for invisible corrosion caused by microorganisms" conducted from FY2020 to FY2022. The present study aims to develop innovative diagnostic techniques such as accelerated test specimens and on-site genetic testing for microbially induced and accelerated corrosion of metallic materials (microbially influenced corrosion, MIC), and to identify the conditions that promote MIC at 1F for proposing methods to prevent MIC through water quality and environmental control.
Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; National Institute for Materials Science*
JAEA-Review 2022-045, 82 Pages, 2023/01
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2021. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (1F), Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2020, this report summarizes the research results of the "Development of genetic and electrochemical diagnosis and inhibition technologies for invisible corrosion caused by microorganisms" conducted in FY2021. The present study aims to develop innovative diagnostic techniques such as accelerated test specimens and on-site genetic testing for microbially induced and accelerated corrosion of metallic materials (microbially influenced corrosion, MIC), and to identify the conditions that promote MIC at 1F for proposing methods to prevent MIC through water quality and environmental control. We also aim to develop a research base based on materials, microorganisms, and electrochemistry, to develop technologies that can be used by engineers in the field, …
Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; The University of Tokyo*
JAEA-Review 2022-015, 119 Pages, 2022/09
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2020. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2018, this report summarizes the research results of the "Analysis of microparticles generated by laser processing and development of a methodology for their nuclear identification" conducted from FY2018 to FY2021 (this contract was extended to FY2021). Since the final year of this proposal was FY2021, the results for four fiscal years were summarized. Although laser processing has various advantages, one well-known disadvantage is that it generates a large amount of microparticles during the processing. Therefore, the application of laser processing to decommissioning waste contaminated with radioactive materials has been hesitant because the mechanism generating the microparticles has not been fully understood.
Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; National Institute for Materials Science*
JAEA-Review 2021-059, 71 Pages, 2022/02
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2020. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (1F), Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2020, this report summarizes the research results of the "Development of genetic and electrochemical diagnosis and inhibition technologies for invisible corrosion caused by microorganisms" conducted in FY2020. The present study aims to develop innovative diagnostic techniques such as accelerated test specimens and on-site genetic testing for microbially induced and accelerated corrosion of metallic materials (microbially influenced corrosion, MIC), and to identify the conditions that promote MIC at 1F for proposing methods to prevent MIC through water quality and environmental control.
Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; The University of Tokyo*
JAEA-Review 2020-031, 69 Pages, 2021/01
JAEA/CLADS had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project in FY2019. Among the adopted proposals in FY2018, this report summarizes the research results of the "Analysis of microparticles generated by laser processing and development of a methodology for their nuclear identification" conducted in FY2019.
Ishimaru, Tsuneari; Ogata, Nobuhisa; Kokubu, Yoko; Shimada, Koji; Hanamuro, Takahiro; Shimada, Akiomi; Niwa, Masakazu; Asamori, Koichi; Watanabe, Takahiro; Sueoka, Shigeru; et al.
JAEA-Research 2020-011, 67 Pages, 2020/10
This annual report documents the progress of research and development (R&D) in the 5th fiscal year during the JAEA 3rd Mid- and Long-term Plan (fiscal years 2015-2021) to provide the scientific base for assessing geosphere stability for long-term isolation of the high-level radioactive waste. The planned framework is structured into the following categories: (1) Development and systematization of investigation techniques, (2) Development of models for long-term estimation and effective assessment, (3) Development of dating techniques. The current status of R&D activities with previous scientific and technological progress is summarized.
Niwa, Masakazu; Ueki, Tadamasa*; Hoshi, Hiroyuki*; Sugisaki, Yuichi*
JAEA-Research 2020-003, 33 Pages, 2020/07
Ages of volcanic rocks are helpful information to understand the impact of volcanism concerning a site characterization and a safety assessment for geological disposal. In this study, mineralogical and geochemical data of altered volcanic rocks were collected using a polarizing microscope, X-ray diffractometer, X-ray fluorescence spectrometer, X-ray analytical microscope, and electron probe microanalyzer, to select targets suitable for reliable K-Ar dating. In addition, sample preparation procedures such as freeze-thawing and HCl treatment were examined to concentrate unaltered plagioclase which is one of major phenocrysts in volcanic rocks. These data and procedures were compiled in this report.
Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; The University of Tokyo*
JAEA-Review 2019-034, 59 Pages, 2020/03
JAEA/CLADS, conducted the Center of World Intelligence Project for Nuclear Science/Technology and Human Resource Development (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2018. The Project aimed to contribute to solving problems in the field of nuclear energy represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development was promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barriers of conventional organizations and research fields. Among the adopted proposals in FY2018, this report summarizes the research results of the "Analysis of microparticles generated by laser processing and development of a methodology for their nuclear identification". Although laser processing has various advantages, one well-known disadvantage is that it generates a large amount of microparticles during the processing. Therefore, the application of laser processing to decommissioning waste contaminated with radioactive materials has been hesitant because the mechanism generating the microparticles has not been fully understood. In this study, the mechanism of microparticle production by laser processing is investigated from fundamentals. Also, we develop a laser on-line principle device to examine the nuclides present in the microparticles that are produced, based on the measurement of the particle size distribution by collecting the microparticles using aerodynamic lenses.
Myagmarjav, O.; Iwatsuki, Jin; Tanaka, Nobuyuki; Noguchi, Hiroki; Kamiji, Yu; Ioka, Ikuo; Kubo, Shinji; Nomura, Mikihiro*; Yamaki, Tetsuya*; Sawada, Shinichi*; et al.
International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 44(35), p.19141 - 19152, 2019/07
Times Cited Count:18 Percentile:46.60(Chemistry, Physical)Saegusa, Jun; Koma, Yoshikazu; Ashida, Takashi
JAEA-Review 2018-017, 259 Pages, 2018/12
Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS) is responsible to promote international cooperation in the R&D activities on the decommissioning of Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station and to develop the necessary human resources. CLADS held the Fukushima Research Conference on Development of Analytical Techniques in Waste Management (FRCWM 2018) on 19th and 20th June, 2018. This report compiles the abstracts and the presentation materials in the above conference.
Komeda, Masao; Ozu, Akira; Mori, Takamasa; Nakatsuka, Yoshiaki; Maeda, Makoto; Kureta, Masatoshi; Toh, Yosuke
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 54(11), p.1233 - 1239, 2017/11
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:60.50(Nuclear Science & Technology)The previous active neutron method cannot remove the influence of the multiplication effect of neutrons produced by second- and subsequent fission reactions, and it might overestimate the amount of nuclear material if an item contains large amounts. In this paper, we discussed the correction method for the neutron multiplication effect on the measured data in the fast neutron direct interrogation (FNDI) method, one of the active neutron methods, supposing that the neutron multiplication effect is caused mainly by third-generation neutrons from the second-fission reactions under the condition that the forth-generation neutrons are much fewer. This paper proposed a correction method for the neutron multiplication effect in the measured data. Moreover we have shown a possibility that this correction method gives rough estimates of the effective neutron multiplication factor and the subcriticality.
Paradela, C.*; Heyse, J.*; Kopecky, S.*; Schillebeeckx, P.*; Harada, Hideo; Kitatani, Fumito; Koizumi, Mitsuo; Tsuchiya, Harufumi
EPJ Web of Conferences, 146, p.09002_1 - 09002_4, 2017/09
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:97.47(Nuclear Science & Technology)Komeda, Masao; Maeda, Makoto; Ozu, Akira; Kureta, Masatoshi; Toh, Yosuke
Proceedings of International Nuclear Fuel Cycle Conference (GLOBAL 2017) (USB Flash Drive), 3 Pages, 2017/09
We have developed a special Nuclear Material Accountancy (NMA) technique using the Fast Neutron Direct Interrogation (FNDI) method which is one of active neutron techniques. A measurement system, for fuel debris at Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, implemented in the simulation was designed as follows. This system has a neutron generator, which can produce neutron yield of 1 10
10 per pulse in 1 kHz repetition rate. The length of the system is 140 cm, and the outer diameter is 80cm. Sixteen He-3 detectors, 100 cm in length and 2.5 cm in diameter, are installed. Simulations were carried out using the Monte Carlo code MVP developed at JAEA. This work provides simulation results and the applicable range of the FNDI method for fuel debris, using various debris model parameters for example, burn-up composition and heterogeneous materials.
per pulse in 1 kHz repetition rate. The length of the system is 140 cm, and the outer diameter is 80cm. Sixteen He-3 detectors, 100 cm in length and 2.5 cm in diameter, are installed. Simulations were carried out using the Monte Carlo code MVP developed at JAEA. This work provides simulation results and the applicable range of the FNDI method for fuel debris, using various debris model parameters for example, burn-up composition and heterogeneous materials.
Seya, Michio; Hajima, Ryoichi*; Kureta, Masatoshi
Proceedings of INMM 58th Annual Meeting (Internet), 10 Pages, 2017/07
Large size freight cargo containers are the most vulnerable items from nuclear security points of view because of their large volume and weight of cargo inside for hiding heavily shielded objects. For strengthening nuclear security, secure detection of NMs in heavily shielded objects, and safe handling (dismantlement) of detected (suspicious) objects, are essential. These require secure detection of NMs, inspection of detailed interior structures of detected objects, rough characterization of NMs (for nuclear bomb or RDD etc.) and confirmation of existence of explosives etc. By using information obtained by these inspections, safe dismantlement of objects is possible. In this paper, we propose a combination of X-ray scanning system with NRF-based NDD system using monochromatic  -ray beam for a secure detection and interior inspections. We also we propose active neutron NDA system using a DT source for interior inspection of NM part.
-ray beam for a secure detection and interior inspections. We also we propose active neutron NDA system using a DT source for interior inspection of NM part.
 Ca +
Ca +  Cm collisions 10% above the Coulomb barrier
Cm collisions 10% above the Coulomb barrierG tz, M.*; G
tz, M.*; G tz, S.*; Kratz, J. V.*; D
tz, S.*; Kratz, J. V.*; D llmann, Ch. E.*; Mokry, Ch.*; Runke, J.*; Th
llmann, Ch. E.*; Mokry, Ch.*; Runke, J.*; Th rle-Pospiech, P.*; Wiehl, N.*; Sch
rle-Pospiech, P.*; Wiehl, N.*; Sch del, M.; Ballof, J.*; et al.
del, M.; Ballof, J.*; et al.
Nuclear Physics A, 961, p.1 - 21, 2017/05
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:55.59(Physics, Nuclear)The kinematics of multi-nucleon transfer reactions in the  Ca +
Ca +  Cm collisions were investigated using a stacked-foil technique and radiochemical separations. In previous studies, isotopic distributions of the products of below-target isotopes were found to be broader than those of above-target isotopes, which had been interpreted as larger contributions of strongly dumped collisions in the productions of below-target isotopes than above-target ones. However, in the present study, the average total kinetic energy loss (TKEL), and thus, the average excitation energies were determined for both below-target and above-target isotopes, and they were found to be similar. This contradicts the previous interpretation, and thus, a new interpretation has been proposed; highly excited above-target products are lost by fission.
Cm collisions were investigated using a stacked-foil technique and radiochemical separations. In previous studies, isotopic distributions of the products of below-target isotopes were found to be broader than those of above-target isotopes, which had been interpreted as larger contributions of strongly dumped collisions in the productions of below-target isotopes than above-target ones. However, in the present study, the average total kinetic energy loss (TKEL), and thus, the average excitation energies were determined for both below-target and above-target isotopes, and they were found to be similar. This contradicts the previous interpretation, and thus, a new interpretation has been proposed; highly excited above-target products are lost by fission.
Ishimaru, Tsuneari; Umeda, Koji*; Yasue, Kenichi; Kokubu, Yoko; Niwa, Masakazu; Asamori, Koichi; Watanabe, Takahiro; Yokoyama, Tatsunori; Fujita, Natsuko; Shimizu, Mayuko; et al.
JAEA-Research 2016-023, 91 Pages, 2017/02
This annual report documents the progress of research and development (R&D) in the 1st fiscal year during the JAEA 3rd Mid- and Long-term Plan (fiscal years 2015-2021) to provide the scientific base for assessing geosphere stability for long-term isolation of the high-level radioactive waste. The planned framework is structured into the following categories: (1) Development and systematization of investigation techniques, (2) Development of models for long-term estimation and effective assessment, (3) Development of dating techniques. In this paper, the current status of R&D activities with previous scientific and technological progress is summarized.
Komeda, Masao; Maeda, Makoto; Furutaka, Kazuyoshi; Tobita, Hiroshi; Hattori, Kentaro; Shimofusa, Taichi; Ozu, Akira; Kureta, Masatoshi
Proceedings of INMM 57th Annual Meeting (Internet), 10 Pages, 2016/07
We are working on the development of a non-destructive assay (NDA) measurement system using the Fast Neutron Direct Interrogation (FNDI) method. The FNDI method is a kind of active neutron technique and can measure the total amounts of fissile materials (U-235, Pu-239, Pu-241). We have already carried out design analyses of an NDA measurement system for measuring the debris assuming use of the Three Mile Island (TMI) canister model. The result was presented at the Institute of Nuclear Materials Management (INMM) 56th Annual Meeting. Since then, we have modified the design of the NDA measurement system for the fuel debris and canister models at 1F. In this paper, we provide the calculation and evaluation results using the modified NDA measurement system. Moreover, we provide analytical investigations of the influence of fuel debris including high fissile material content on measurements.
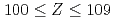 from alpha spectroscopy
from alpha spectroscopyAsai, Masato; He berger, F. P.*; Lopez-Martens, A.*
berger, F. P.*; Lopez-Martens, A.*
Nuclear Physics A, 944, p.308 - 332, 2015/12
Times Cited Count:61 Percentile:95.54(Physics, Nuclear)Nuclear structure of Z = 100-109 nuclei studied through  -decay spectroscopy have been reviewed. Experimental techniques and methods concerning separation techniques, summing effects in
-decay spectroscopy have been reviewed. Experimental techniques and methods concerning separation techniques, summing effects in  spectra, and the use of digital electronics for
spectra, and the use of digital electronics for  -decay spectroscopy have been described in detail. The presentation of the experimental results and the physics discussion were focused on nuclear structure systematics in even-Z nuclei along the N = 151, 153, and 155 isotonic lines, where most progress has been achieved in the last 10 years.
-decay spectroscopy have been described in detail. The presentation of the experimental results and the physics discussion were focused on nuclear structure systematics in even-Z nuclei along the N = 151, 153, and 155 isotonic lines, where most progress has been achieved in the last 10 years.